作者简介
杨奇龙,网名“北在南方”,7年DBA老兵,目前任职于杭州有赞科技DBA,主要负责数据库架构设计和运维平台开发工作,擅长数据库性能调优、故障诊断。
func (this *Migrator) Migrate() //Migrate executes the complete migration logic. This is the major gh-ost function.
a 测试db是否可连通,
b 权限验证
show grants for current_user()
c 获取binlog相关信息,包括row格式和修改binlog格式后的重启replicate
select @@global.log_bin, @@global.binlog_format
select @@global.binlog_row_image
d 原表存储引擎是否是innodb,检查表相关的外键,是否有触发器,行数预估等操作,需要注意的是行数预估有两种方式 一个是通过explain 读执行计划 另外一个是select count(*) from table ,遇到几百G的大表,后者一定非常慢。
explain select /* gh-ost */ * from `test`.`b` where 1=1
2019-09-08T22:01:20.944172+08:00 17760 Query show /* gh-ost readCurrentBinlogCoordinates */ master status
2019-09-08T22:01:20.947238+08:00 17762 Connect root@127.0.0.1 on using TCP/IP
2019-09-08T22:01:20.947349+08:00 17762 Query SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'BINLOG_CHECKSUM'
2019-09-08T22:01:20.947909+08:00 17762 Query SET @master_binlog_checksum='NONE'
2019-09-08T22:01:20.948065+08:00 17762 Binlog Dump Log: 'mysql-bin.000005' Pos: 795282
xx_ghc 和影子表 xx_gho 并且执行 alter 语句将影子表变更为目标表结构。如下日志记录了该过程,gh-ost 会将核心步骤记录到 _b_ghc 中。
2019-09-08T22:01:20.954866+08:00 17760 Query create /* gh-ost */ table `test`.`_b_ghc` (
id bigint auto_increment,
last_update timestamp not null DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
hint varchar(64) charset ascii not null,
value varchar(4096) charset ascii not null,
primary key(id),
unique key hint_uidx(hint)
) auto_increment=256
2019-09-08T22:01:20.957550+08:00 17760 Query create /* gh-ost */ table `test`.`_b_gho` like `test`.`b`
2019-09-08T22:01:20.960110+08:00 17760 Query alter /* gh-ost */ table `test`.`_b_gho` engine=innodb
2019-09-08T22:01:20.966740+08:00 17760 Query
insert /* gh-ost */ into `test`.`_b_ghc`(id, hint, value)values (NULLIF(2, 0), 'state', 'GhostTableMigrated') on duplicate key update last_update=NOW(),value=VALUES(value)
4. insert into xx_gho select * from xx 拷贝数据
获取最小主键 select `id` from `test`.`b` order by `id` asc limit 1;
获取最大主键 soelect `id` from `test`.`b` order by `id` desc limit 1;
获取第一个 chunk:
select /* gh-ost `test`.`b` iteration:0 */ `id` from `test`.`b` where ((`id` > _binary'1') or ((`id` = _binary'1'))) and ((`id` < _binary'21') or ((`id` = _binary'21'))) order by `id` asc limit 1 offset 999;
循环插入到目标表:
insert /* gh-ost `test`.`b` */ ignore into `test`.`_b_gho` (`id`, `sid`, `name`, `score`, `x`) (select `id`, `sid`, `name`, `score`, `x` from `test`.`b` force index (`PRIMARY`) where (((`id` > _binary'1') or ((`id` = _binary'1'))) and ((`id` < _binary'21') or ((`id` = _binary'21')))) lock in share mode;
循环到最大的id,之后依赖binlog 增量同步
rowcopy 过程中是对原表加上 lock in share mode,防止数据在 copy 的过程中被修改。这点对后续理解整体的数据迁移非常重要。因为 gh-ost 在 copy 的过程中不会修改这部分数据记录。对于解析 binlog 获得的 INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE 事件我们只需要分析 copy 数据之前 log before copy 和 copy 数据之后 log after copy。整体的数据迁移会在后面做详细分析。
核心代码在 gh-ost/go/sql/builder.go 中,这里主要做 DML 转换的解释,当然还有其他函数做辅助工作,比如数据库,表名校验 以及语法完整性校验。
func BuildDMLDeleteQuery(databaseName, tableName string, tableColumns, uniqueKeyColumns *ColumnList, args []interface{}) (result string, uniqueKeyArgs []interface{}, err error) {
....省略代码...
result = fmt.Sprintf(`
delete /* gh-ost %s.%s */
from
%s.%s
where
%s
`, databaseName, tableName,
databaseName, tableName,
equalsComparison,
)
return result, uniqueKeyArgs, nil
}
解析到 insert 语句对应转换为 replace into 语句
func BuildDMLInsertQuery(databaseName, tableName string, tableColumns, sharedColumns, mappedSharedColumns *ColumnList, args []interface{}) (result string, sharedArgs []interface{}, err error) {
....省略代码...
result = fmt.Sprintf(`
replace /* gh-ost %s.%s */ into
%s.%s
(%s)
values
(%s)
`, databaseName, tableName,
databaseName, tableName,
strings.Join(mappedSharedColumnNames, ", "),
strings.Join(preparedValues, ", "),
)
return result, sharedArgs, nil
}
func BuildDMLUpdateQuery(databaseName, tableName string, tableColumns, sharedColumns, mappedSharedColumns, uniqueKeyColumns *ColumnList, valueArgs, whereArgs []interface{}) (result string, sharedArgs, uniqueKeyArgs []interface{}, err error) {
....省略代码...
result = fmt.Sprintf(`
update /* gh-ost %s.%s */
%s.%s
set
%s
where
%s
`, databaseName, tableName,
databaseName, tableName,
setClause,
equalsComparison,
)
return result, sharedArgs, uniqueKeyArgs, nil
}
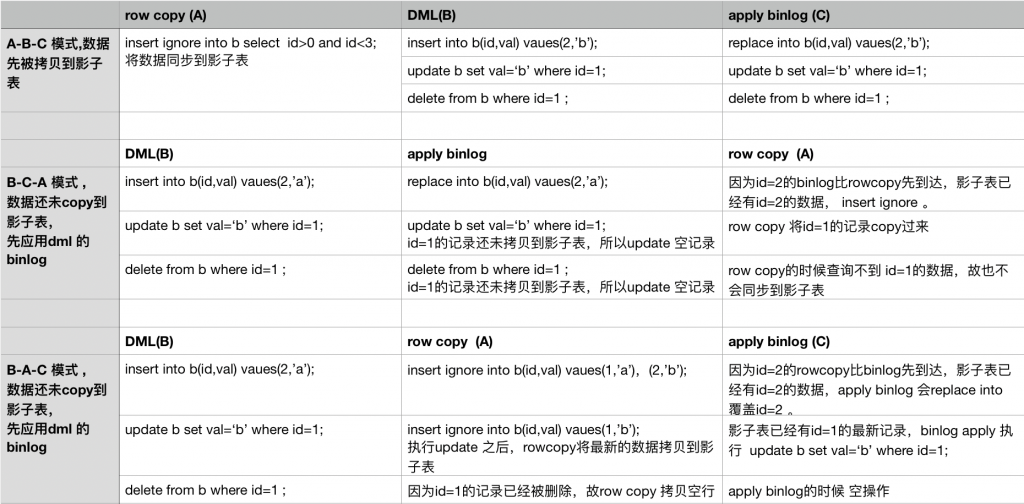
通过上面的几种组合操作的分析,我们可以看到数据最终是一致的。尤其是当copy 结束之后,只剩下apply binlog,情况更简单。
http://code.openark.org/blog/mysql/solving-the-non-atomic-table-swap-take-iii-making-it-atomic
Solving the non-atomic table swap, Take IIhttp://code.openark.org/blog/mysql/solving-the-facebook-osc-non-atomic-table-swap-problem
1 会话 c1..c9: 对b表正常执行DML操作。
2 会话 c10 : 创建_b_del 防止提前rename 表,导致数据丢失。
create /* gh-ost */ table `test`.`_b_del` (
id int auto_increment primary key
) engine=InnoDB comment='ghost-cut-over-sentry'
3 会话 c10 执行LOCK TABLES b WRITE, `_b_del` WRITE。
4 会话c11-c19 新进来的dml或者select请求,但是会因为表b上有锁而等待。
5 会话c20:设置锁等待时间并执行rename
set session lock_wait_timeout:=1
rename /* gh-ost */ table `test`.`b` to `test`.`_b_20190908220120_del`, `test`.`_b_gho` to `test`.`b`
c20 的操作因为c10锁表而等待。
6 c21-c29 对于表 b 新进来的请求因为lock table和rename table 而等待。
7 会话c10 通过sql 检查会话c20 在执行rename操作并且在等待mdl锁。
select id
from information_schema.processlist
where
id != connection_id()
and 17765 in (0, id)
and state like concat('%', 'metadata lock', '%')
and info like concat('%', 'rename', '%')
8 c10 基于步骤7 执行drop table `_b_del` ,删除命令执行完,b表依然不能写。所有的dml请求都被阻塞。
9 c10 执行UNLOCK TABLES; 此时c20的rename命令第一个被执行。而其他会话c1-c9,c11-c19,c21-c29的请求可以操作新的表b。
划重点(敲黑板)
1. 创建
_b_del表是为了防止 cut-over 提前执行,导致数据丢失。2. 同一个会话先执行 write lock 之后还是可以 drop 表的。
3. 无论 rename table 和 DML 操作谁先执行,被阻塞后 rename table 总是优先于 DML 被执行。大家可以一边自己执行 gh-ost ,一边开启 general log 查看具体的操作过程。
2019-09-08T22:01:24.086734 17765 create /* gh-ost */ table `test`.`_b_20190908220120_del` (
id int auto_increment primary key
) engine=InnoDB comment='ghost-cut-over-sentry'
2019-09-08T22:01:24.091869 17760 Query lock /* gh-ost */ tables `test`.`b` write, `test`.`_b_20190908220120_del` write
2019-09-08T22:01:24.188687 17765 START TRANSACTION
2019-09-08T22:01:24.188817 17765 select connection_id()
2019-09-08T22:01:24.188931 17765 set session lock_wait_timeout:=1
2019-09-08T22:01:24.189046 17765 rename /* gh-ost */ table `test`.`b` to `test`.`_b_20190908220120_del`, `test`.`_b_gho` to `test`.`b`
2019-09-08T22:01:24.192293+08:00 17766 Connect root@127.0.0.1 on test using TCP/IP
2019-09-08T22:01:24.192409 17766 SELECT @@max_allowed_packet
2019-09-08T22:01:24.192487 17766 SET autocommit=true
2019-09-08T22:01:24.192578 17766 SET NAMES utf8mb4
2019-09-08T22:01:24.192693 17766 select id
from information_schema.processlist
where
id != connection_id()
and 17765 in (0, id)
and state like concat('%', 'metadata lock', '%')
and info like concat('%', 'rename', '%')
2019-09-08T22:01:24.193050 17766 Query select is_used_lock('gh-ost.17760.lock')
2019-09-08T22:01:24.193194 17760 Query drop /* gh-ost */ table if exists `test`.`_b_20190908220120_del`
2019-09-08T22:01:24.194858 17760 Query unlock tables
2019-09-08T22:01:24.194965 17760 Query ROLLBACK
2019-09-08T22:01:24.197563 17765 Query ROLLBACK
2019-09-08T22:01:24.197594 17766 Query show /* gh-ost */ table status from `test` like '_b_20190908220120_del'
2019-09-08T22:01:24.198082 17766 Quit
2019-09-08T22:01:24.298382 17760 Query drop /* gh-ost */ table if exists `test`.`_b_ghc`
如果c10的create `_b_del` 失败,gh-ost 程序退出。
如果c10的加锁语句失败,gh-ost 程序退出,因为表还未被锁定,dml请求可以正常进行。
如果c10在c20执行rename之前出现异常
A. c10持有的锁被释放,查询c1-c9,c11-c19的请求可以立即在b执行。
B. 因为`_b_del`表存在,c20的rename table b to `_b_del`会失败。
C. 整个操作都失败了,但没有什么可怕的事情发生,有些查询被阻止了一段时间,我们需要重试。
如果c10在c20执行rename被阻塞时失败退出,与上述类似,锁释放,则c20执行rename操作因为——b_old表存在而失败,所有请求恢复正常。
如果c20异常失败,gh-ost会捕获不到rename,会话c10继续运行,释放lock,所有请求恢复正常。
如果c10和c20都失败了,没问题:lock被清除,rename锁被清除。c1-c9,c11-c19,c21-c29可以在b上正常执行。
slave 因为 binlog 文件中不会复制 lock 语句,只能应用 rename 语句进行原子操作,对复制无损。
7. 处理收尾工作
关闭 binlogsyncer 连接 至于中间表,其实和参数有关 --initially-drop-ghost-table--initially-drop-old-table
社区近期动态
No.1
10.26 DBLE 用户见面会 北京站

爱可生开源社区将在 2019 年 10 月 26 日迎来在北京的首场 DBLE 用户见面会,以线下互动分享的会议形式跟大家见面。
时间:10月26日 9:00 – 12:00 AM
地点:HomeCafe 上地店(北京市海淀区上地二街一号龙泉湖酒店对面)
重要提醒:
1. 同日下午还有 dbaplus 社群举办的沙龙:聚焦数据中台、数据架构与优化。
2. 爱可生开源社区会在每年10.24日开源一款高质量产品。本次在 dbaplus 沙龙会议上,爱可生的资深研发工程师闫阿龙,将为大家带来《金融分布式事务实践及txle概述》,并在现场开源。
No.2
Mycat 问题免费诊断
诊断范围支持:
Mycat 的故障诊断、源码分析、性能优化
服务支持渠道:
技术交流群,进群后可提问
QQ群(669663113)
社区通道,邮件&电话
osc@actionsky.com
现场拜访,线下实地,1天免费拜访
关注“爱可生开源社区”公众号,回复关键字“Mycat”,获取活动详情。
No.3
社区技术内容征稿
征稿内容:
格式:.md/.doc/.txt
主题:MySQL、分布式中间件DBLE、数据传输组件DTLE相关技术内容
要求:原创且未发布过
奖励:作者署名;200元京东E卡+社区周边
投稿方式:
邮箱:osc@actionsky.com
格式:[投稿]姓名+文章标题
以附件形式发送,正文需注明姓名、手机号、微信号,以便小编及时联系